The field of robotics has made tremendous strides in recent years, with humanoid robots being at the forefront of innovation. In 2024, humanoid robots are transitioning from research prototypes to practical applications.
In this article we’ll take a look at the current state of humanoid robots, exploring their advancements, challenges, and potential applications that are transforming industries and revolutionizing the way we live.
Advancements in Humanoid Robotics
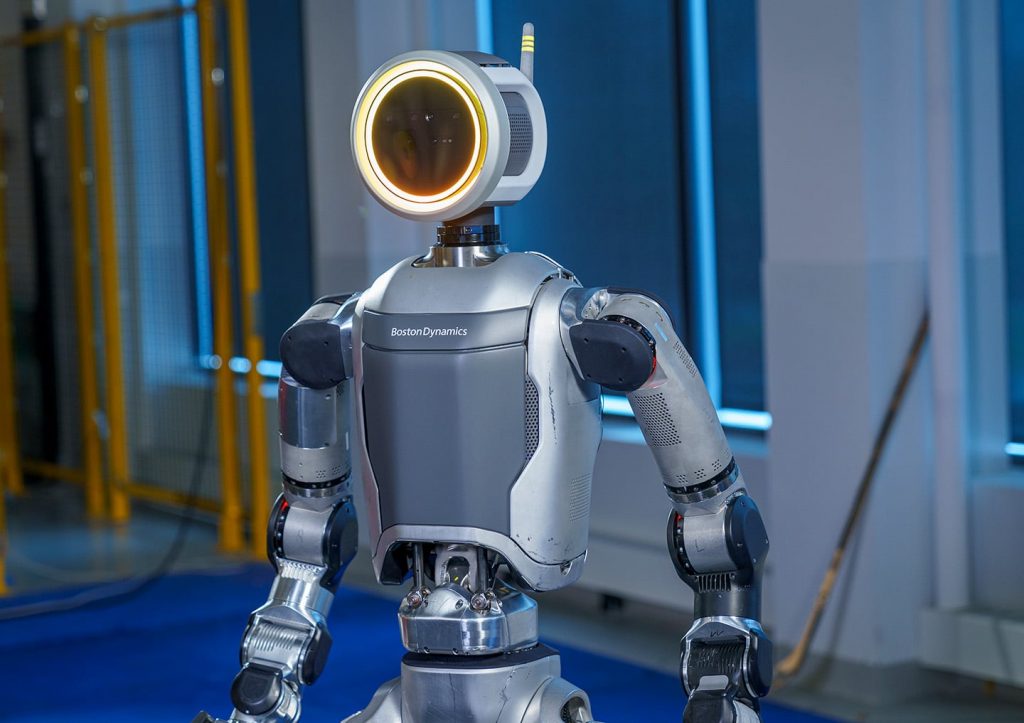

Improved Design and Materials – Space Age Metals and 3D Printing
Humanoid robots have undergone significant design enhancements, with a focus on creating more human-like appearances and capabilities. Advanced materials and 3D printing technologies have enabled the development of lighter, stronger, and more durable robots.
One of the leaders in the field is Boston Dynamics. The company has seen several of its videos over the years go viral, and they often star their Atlas humanoid robot. In April 2024, BD unveiled the latest Atlas, with a fully electric custom battery and innovative hydraulic system, one of the most compact in the world. It enables the robot to perform remarkable feats of agility and strength.
Atlas features 28 hydraulic joints, allowing for a wide range of motion and flexibility. Its advanced control algorithms enable the robot to plan and execute complex whole-body movements, taking into account its surroundings and environment.

With a top speed of 2.5 meters per second, Atlas is capable of rapid movements and quick reflexes. Its lightweight design, achieved through the use of titanium and aluminum 3D printed parts, provides a superior strength-to-weight ratio, allowing the robot to perform impressive jumps and somersaults.
Enhanced Sensing and Perception
Humanoid robots are now equipped with advanced sensing and perception capabilities, including high-resolution cameras, lidar sensors, and tactile sensors. These sensors enable robots to better understand their environment, detect obstacles, and interact with humans more effectively. SoftBank’s Pepper, a humanoid robot used in customer service, employs advanced sensors to recognize and respond to human emotions. According to the company, “Pepper can make personalized recommendations, help people find exactly what they’re looking for, sell, upsell, and cross-sell, and interact with your human team as needed.”

Advanced Actuation and Control
Breakthroughs in actuation and control systems have improved the agility, flexibility, and precision of humanoid robots.
In robotics, an actuator is a device that enables a robot to move and perform tasks by converting stored energy into movement. They are typically powered by air, electricity, or liquids. Actuators play a crucial role in robotics, enabling robots to interact with their environment, sense and respond to stimuli and perform a wide range of tasks. Advanced actuators, such as electric motors and hydraulic systems, provide faster and more accurate movements, while sophisticated control algorithms enable robots to adapt to changing situations.
UBTech’s Walker X, a humanoid robot designed for logistics and warehousing, demonstrates impressive agility and dexterity.
Increased Autonomy and Learning
Humanoid robots are becoming increasingly autonomous, with the ability to learn from experiences and adapt to new situations. Advanced machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence enable robots to make decisions, navigate complex environments, and interact with humans in a more natural way.
One example is Figure 01. OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, has partnered partnership with California robotics startup Figure, aiming to integrate its AI systems into humanoid robots. Figure envisions deploying human-like robots in workplaces and homes on a massive scale. CEO Brett Adcock believes that addressing labor shortages by deploying robots could lead to selling millions or even billions of units.
This collaboration represents a shift for OpenAI, and will involve OpenAI developing specialized AI models, likely based on its existing technologies such as GPT language models, DALL-E image generator, and Sora video generator, to enhance Figure’s humanoid robots. This integration aims to enable the robots to process and reason from language, potentially accelerating Figure’s commercial timeline.
Challenges and Limitations

Safety and Security
As humanoid robots become more advanced, ensuring their safety and security is crucial. Developers must address concerns around robot-human collisions, data privacy, and potential misuse.
Cost and Affordability
The high cost of humanoid robots remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Reducing costs while maintaining performance is essential for commercial viability.
British firm Engineered Arts allows two options on its robots. Their Ameca roboto is currently is available for purchase or event rental.
“As well as a development platform, Ameca is also a great attraction, just like our Mesmer and RoboThespian robots. Wow your customers or visitors at an event or visitor attraction. Reliability is key, and all our robots are built to last in action in the real world, not just in the lab.”
Social Acceptance
Humanoid robots raise important social and ethical questions, such as job displacement, privacy, and accountability. Addressing these concerns through transparent development and deployment practices is vital. The IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems provides guidelines for responsible robot development.

Humanoid Robots: Emerging Applications and Industries
Healthcare and Rehabilitation
Humanoid robots are being used in healthcare to assist with patient care, rehabilitation, and therapy. A recent research paper published in the Journal of information Technology Teaching Cases outlines the impact that humanoid service robots (SR) made during the pandemic:
“The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the inclusion of humanoid SR in healthcare. The suddenly increasing demand in healthcare nurtured an atmosphere where any possible help was embraced. Moreover, the possibility to minimize or eliminate contact with patients promoted an opportunity to protect the precious healthcare workforce from contracting the virus. The scarcity observed in personal protective equipment (PPE) was also minimized. By eliminating the need for donning and doffing PPE, which also included a time-consuming protocol to wear and take off, doctors and nurses were provided with more time to dedicate to their patients, too. When hospital visits were no longer a possibility, humanoid SR helped with connecting patients with their families for morale and support.”
Manufacturing and Logistics
Humanoid robots are revolutionizing manufacturing and logistics by performing tasks that require dexterity, flexibility, and adaptability.
One recent example is in automotive. Last month, Mercedes-Benz Group signed a contract with the U.S. robotics supplier Apptronik to use the humanoid robot Apollo in its plant in Kecskemét, Hungary.
Jörg Burzer, head of production at Mercedes-Benz Group told Automotive Logistics that: ”This is a new frontier and we want to understand the potential both for robotics and automotive manufacturing to fill labour gaps in areas such as low skill, repetitive and physically demanding work and to free up our highly skilled team members on the line to build the world’s most desirable cars.”
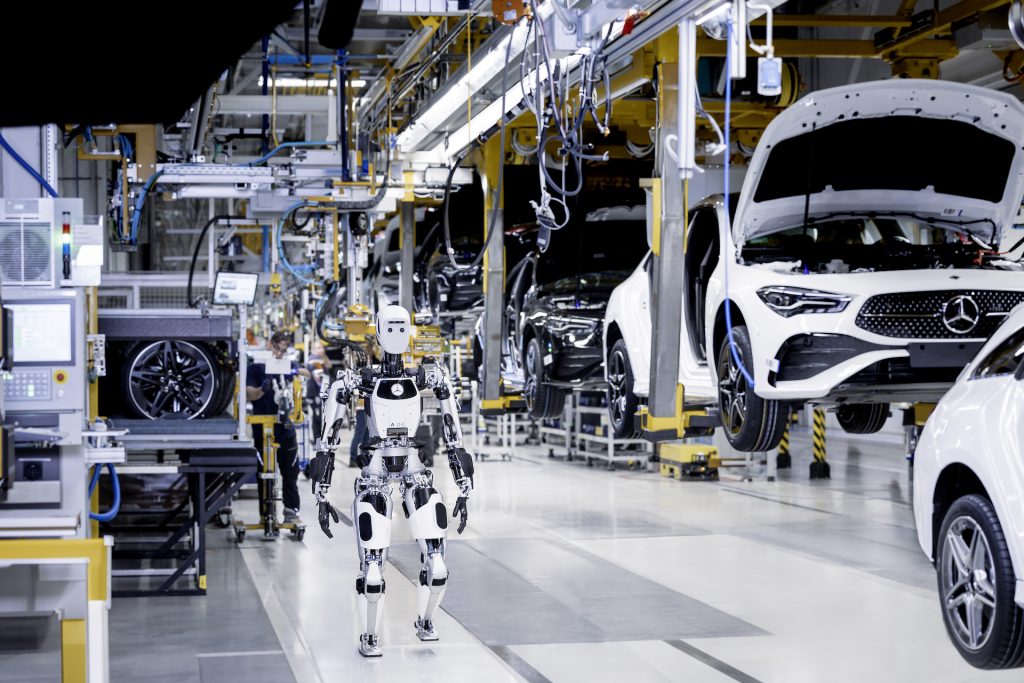

Apollo is built with “force control architecture” – a term which generally means that they are safe to operate around humans.
Apptronik’s CEO Jeff Cardenas stated: “Mercedes plans to use robotics and Apollo for automating some low skill, physically challenging, manual labour – a model use case which we’ll see other organizations replicate in the months and years to come.”
Service and Tourism
The hospitality and service sector is also seeing implementations of humanoid robotics and collaborative robots (cobots). Robots are already being used to make coffee, make hotel beds, and to cook.
One of the most popular is Pepper, the SoftBank cobot discussed earlier in this piece.
A new project by EHL Lausanne, a Swiss hospitality school, has employed Pepper as a robot concierge solution. A true cobot situation, Pepper is controlled by human agent, and it’s appearance makes for a novelty for human’s to interact with.
Another example is Anna, a hybrid AI robot that can clean your home, Airbnb, or hotel room, developed by AnnaOne ApS, a Copenhagen-based robotics company.
Education
Humanoid robots are being used in educational institutions to teach robotics, programming, and STEM subjects. Pepper, mentioned above, is also being used in educational settings, but the most popular robot in the education space is Softbank’s other one: NAO.
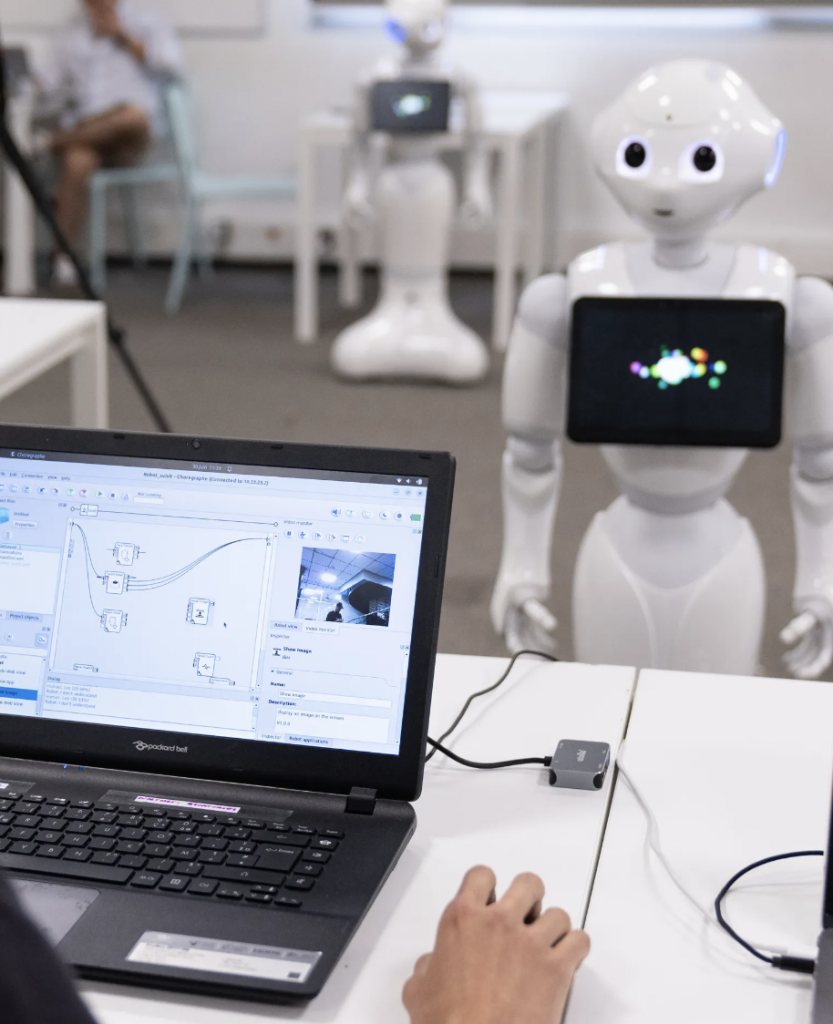

Over the last decade, the Nao robot has been widely adopted by over 200 academic institutions worldwide including universities in the UK, India, Japan, and the US. It has been used in various applications, such as helping to teach students with autism. By 2014, over 5,000 Nao robots were in use across 70 countries.
Today, Nao is available as a research robot for educational institutions to teach programming and conduct research into human-robot interactions. Additionally, online learning platforms have been developed to enhance the use of Nao for STEM, coding, and engineering education.
Scientific Research Applications
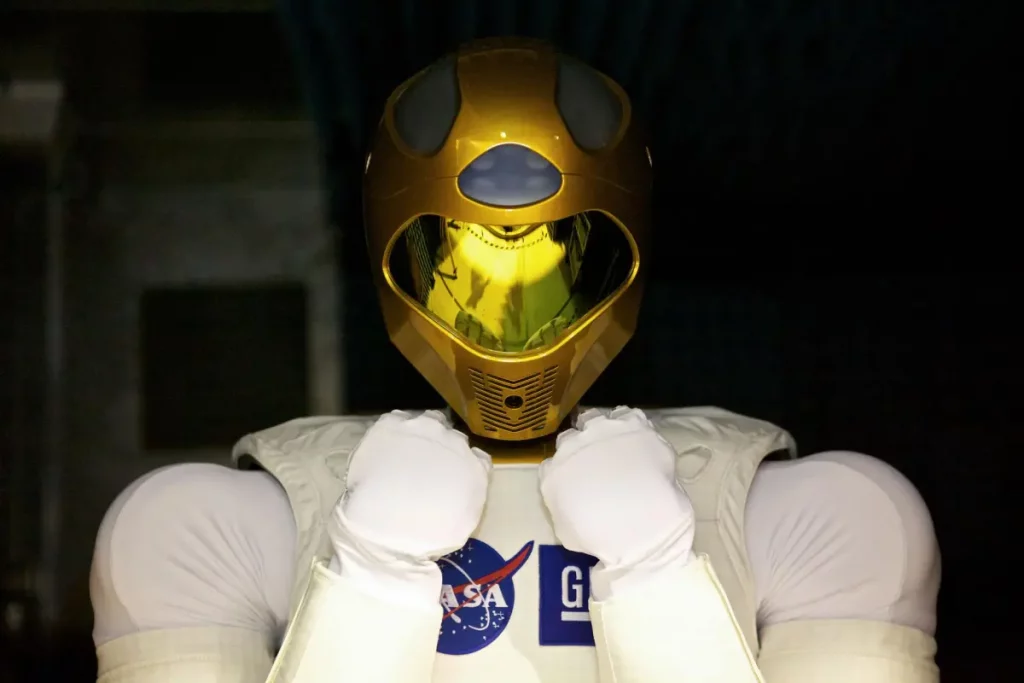

Robots have been deployed in a variety of real-world scientific test scenarios.
Space is one example.
NASA has been in the robotics development for years. In 2011, the space agency deployed Robonaut 2 (R2) aboard the space shuttle Discovery as part of the STS-133 mission. Developed collaboratively by NASA and General Motors, R2 aimed to serve as a permanent resident of the International Space Station. This joint effort aimed to create a robotic assistant capable of working alongside humans, whether in the challenging environment of space or on the factory floors of GM manufacturing plants on Earth.
Another scientific implementation is oceanic exploration.
OceanOneK, a diving bot developed by the Stanford Robotics Lab team, is built to explore the the depths of the ocean, exploring sunken planes, ships, and a submarine, reaching depths of nearly 1 km. Its unique design features a humanoid top half and a slimmer back half with eight multi-directional thrusters for precise underwater navigation.
Operators of OceanOneK experience a remarkable sense of immersion, thanks to its haptic feedback system and stereoscopic vision, enabling them to feel as if they are truly interacting with the deep-sea environment. During its first expedition in the Mediterranean, OceanOneK provided users with a vivid experience of the underwater world, allowing them to perceive the vibrant colors and textures of marine life while feeling the resistance of the water and discerning the shapes and proximity of historic relics surrounding them.

The current state of humanoid robots in 2024 is marked by significant advancements, challenges, and potential applications.
As we continue to push the boundaries of robotics, it’s essential to address the challenges and limitations, ensuring that humanoid robots are developed and deployed responsibly.
With their potential to transform industries and revolutionize the way we live, humanoid robots are an exciting and rapidly evolving field, poised to assist the future of humanity.
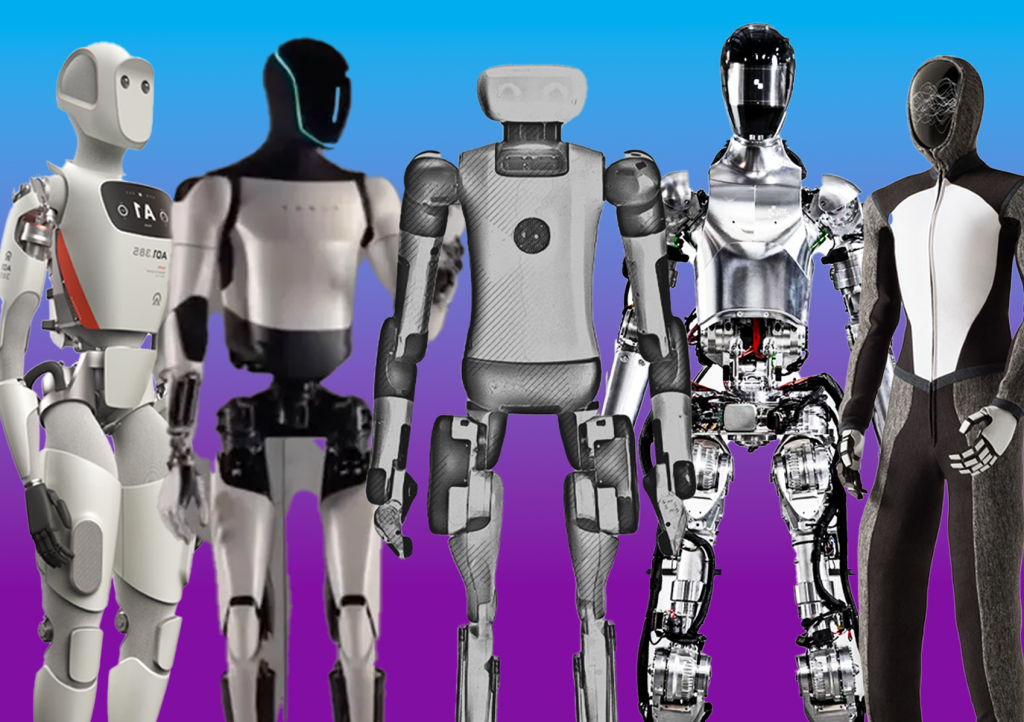
Below is our infographic comparing several of the top humanoid robots in production or development in 2024. Click to zoom.




Pingback: Infographic: Humanoid Robots – THE DEPT OF NEXT